Each year all the calves are named in September after spending the first four months of their lives free-ranging in the Cairngorms. Every year we select a theme to name the calves by. In 2011 the theme was “Games and Past Times”; as a result we have Scrabble, Rubiks, Rummy, Origami, Monopoly, Puzzle and Jenga amongst others.
However, as with any rule there is always an exception and Svalbard, also born in 2011, is the odd one out for that year!
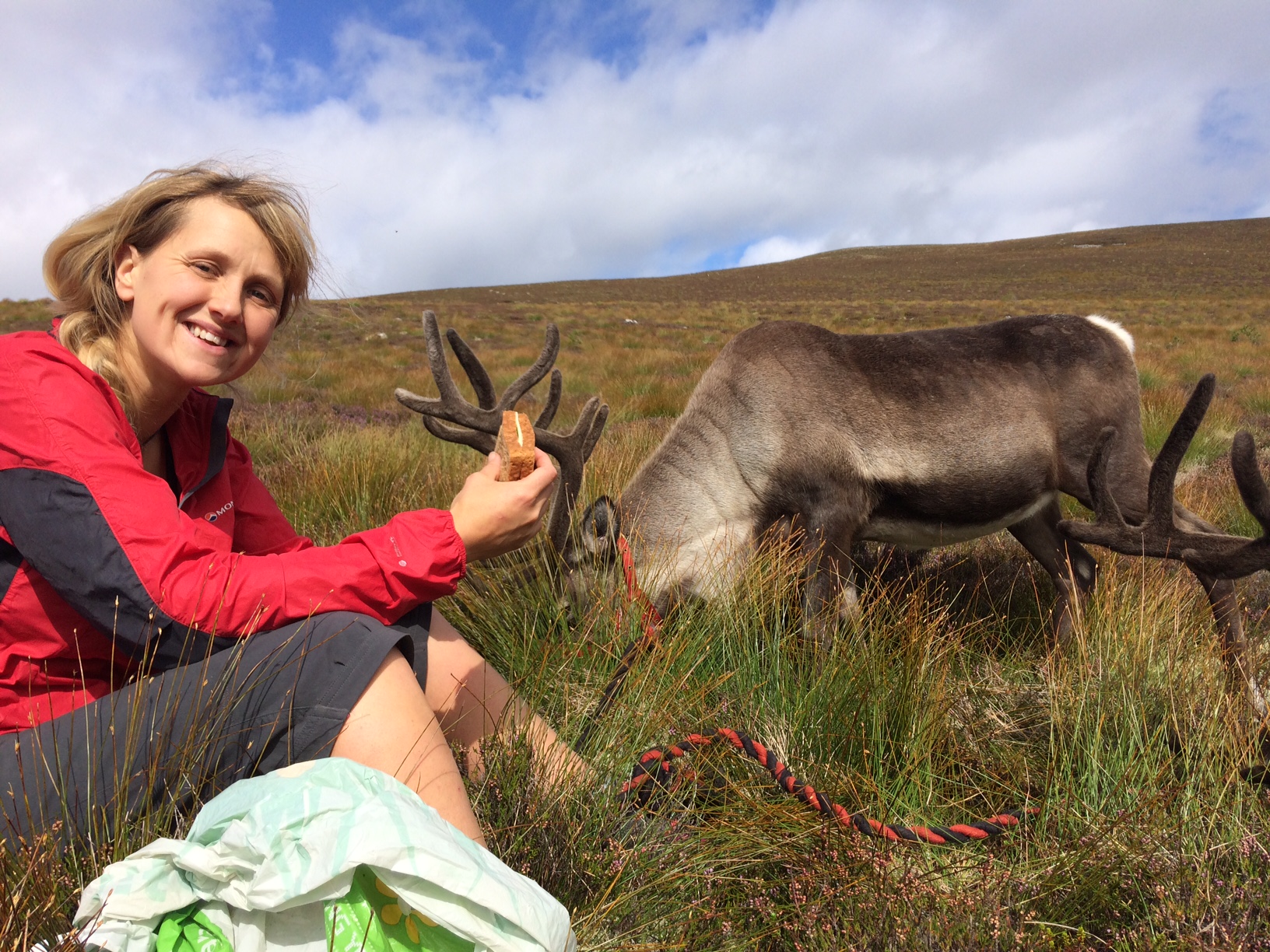
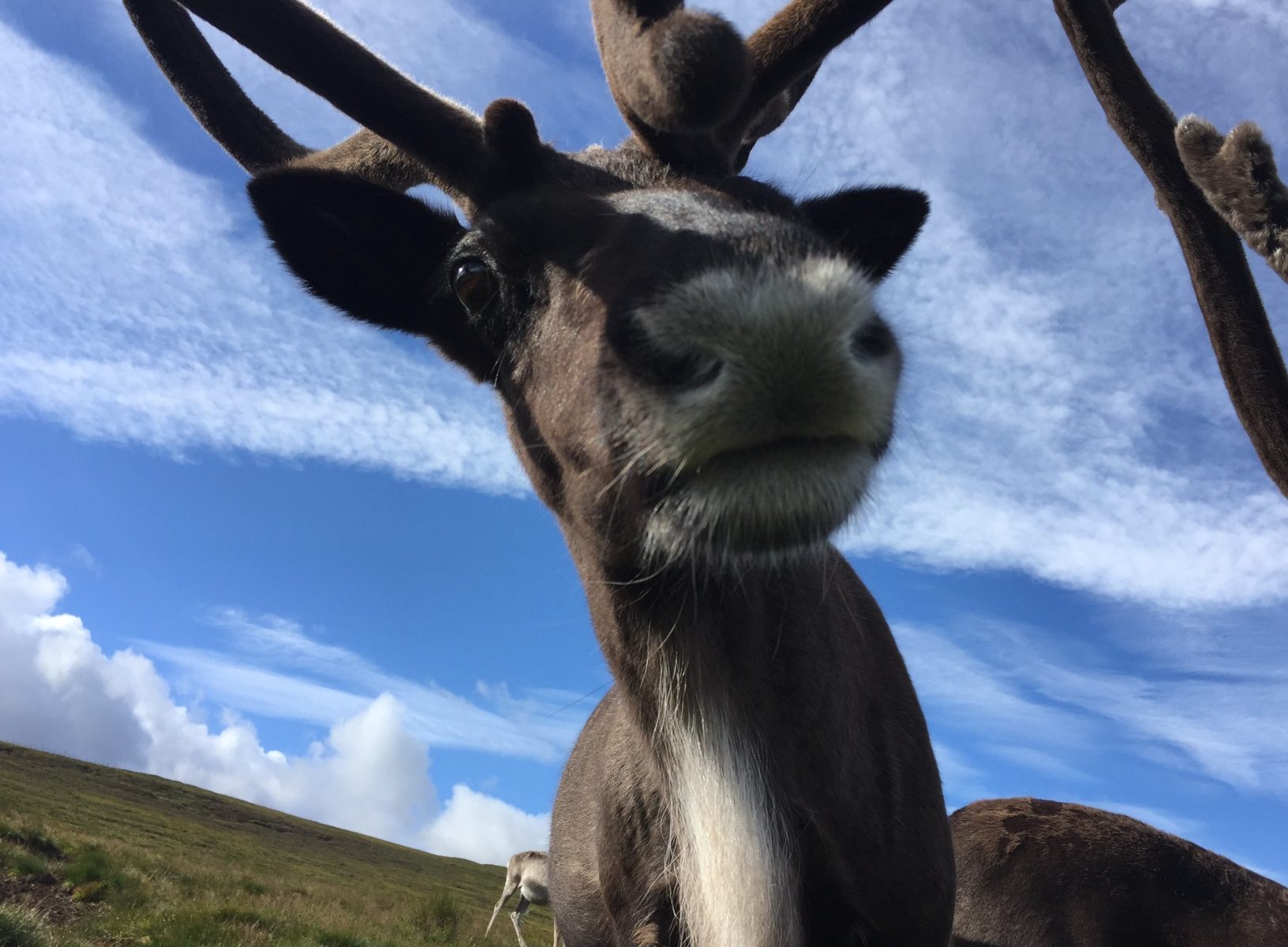
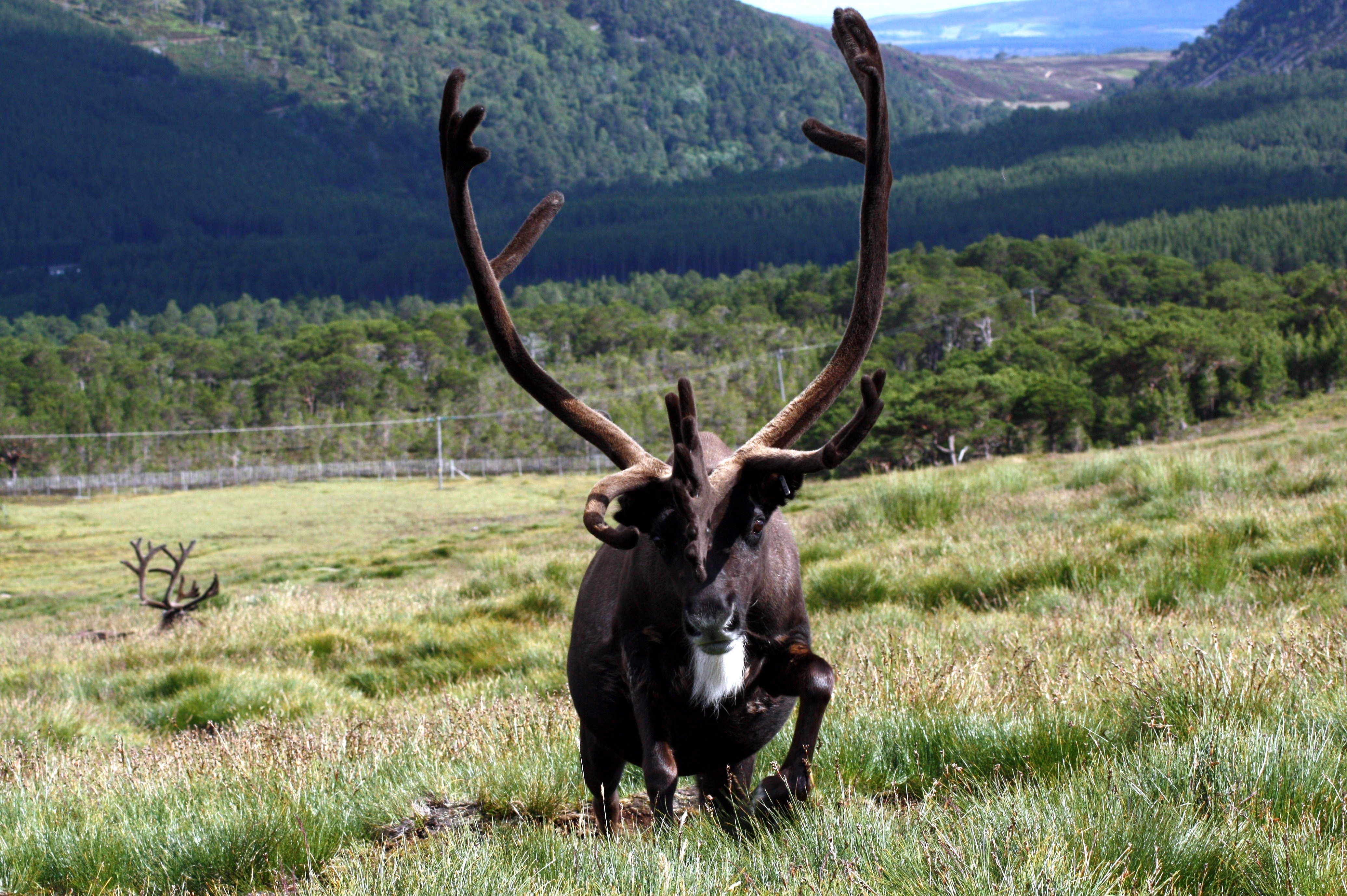
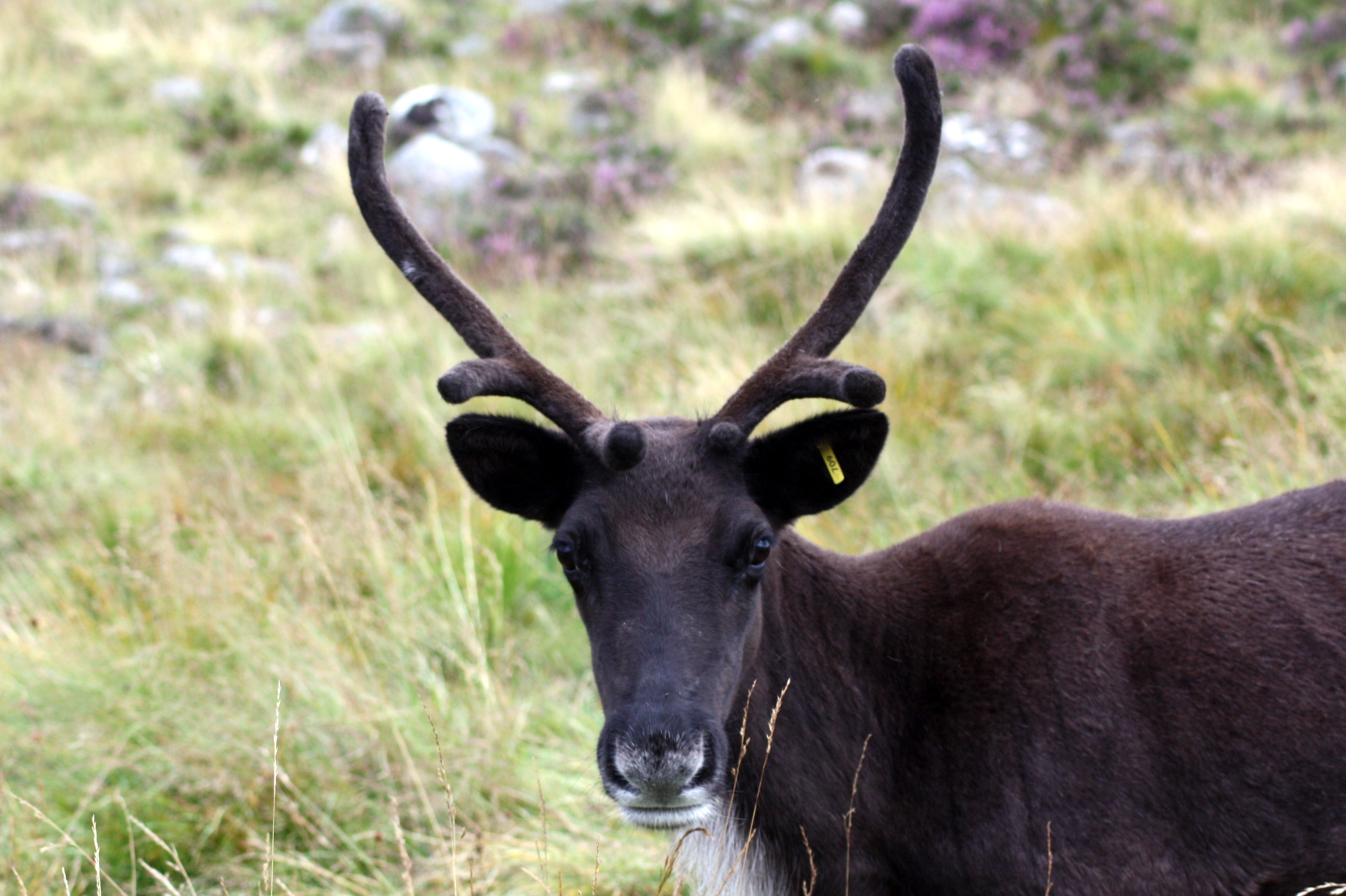
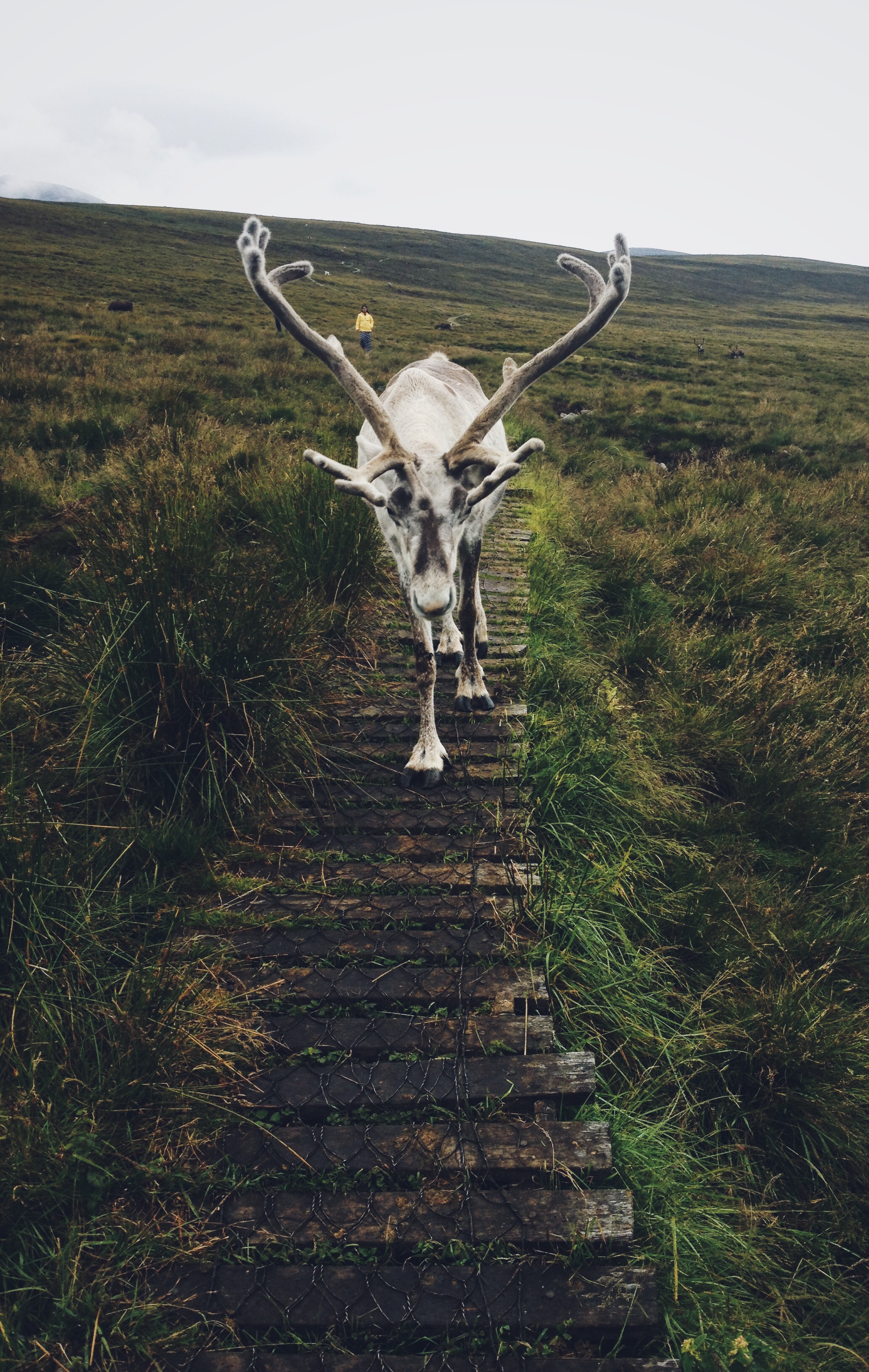
Svalbard is currently in our Hill Enclosure here in the Cairngorms and, because of his large white nose (not to mention his fondness for food), he often stands out leading visitors on our Hill Trips to ask what his name is. This has prompted me to answer the question, why is Svalbard, called Svalbard?!
To fully answer I’m going to first take us to the Arctic Ocean and the archipelago of Svalbard itself…

The Svalbard archipelago of Norway is found in the Arctic Ocean north of mainland Europe, approximately halfway between Norway and the North Pole.
Svalbard is an incredibly wild place with a land area of 61,022 km2 and a human population of only around 2700 (for comparison Scotland’s land area is 77,933 km2). Approximately 60% of the archipelago is covered with glaciers! The islands are home to only a few species of mammal which include polar bear, Arctic fox and its own subspecies of reindeer, called the Svalbard reindeer (Rangifer tarandus platyrhynchus).

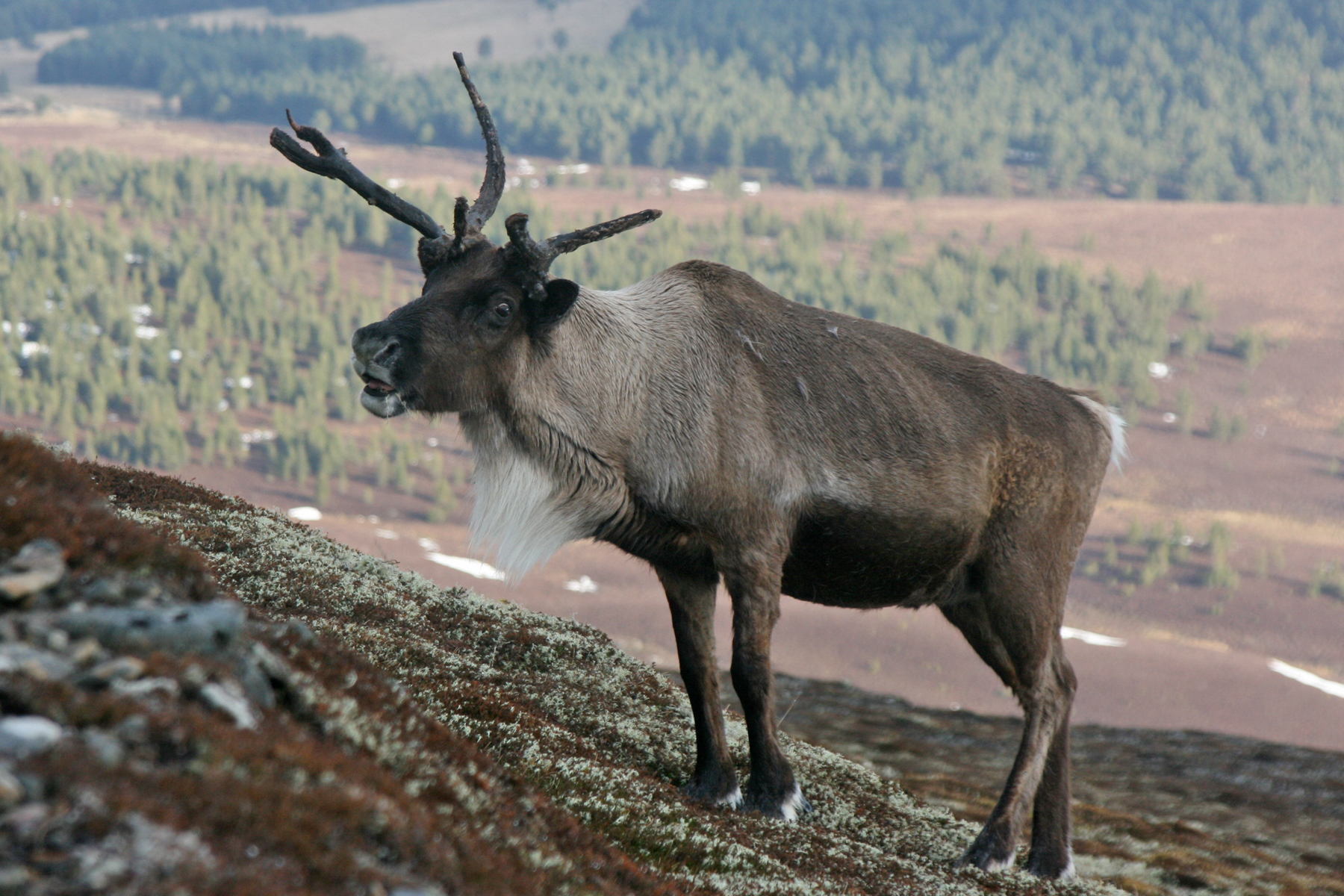
The Svalbard reindeer has inhabited this harsh wilderness, and has been geographically isolated from other reindeer for over 5000 years. As a result they have become very well adapted to the particular landscape and roam on nearly all non-glaciated areas of the archipelago. The Svalbard reindeer wins the award for being the most northerly living herbivore mammal in the world!

The Svalbard reindeer is the smallest subspecies of all reindeer and caribou. Bulls average 65-90kg in weight, and cows between 53-70kg compared with our Cairngorm reindeer where bulls can weigh 150kg. Svalbard reindeer are very distinctive for having short faces and short legs, making them appear ‘dumpy’. They also have a very think, long winter coat. The long coat also contributes to their short-legged appearance and even starved individuals can appear fat in the winter!
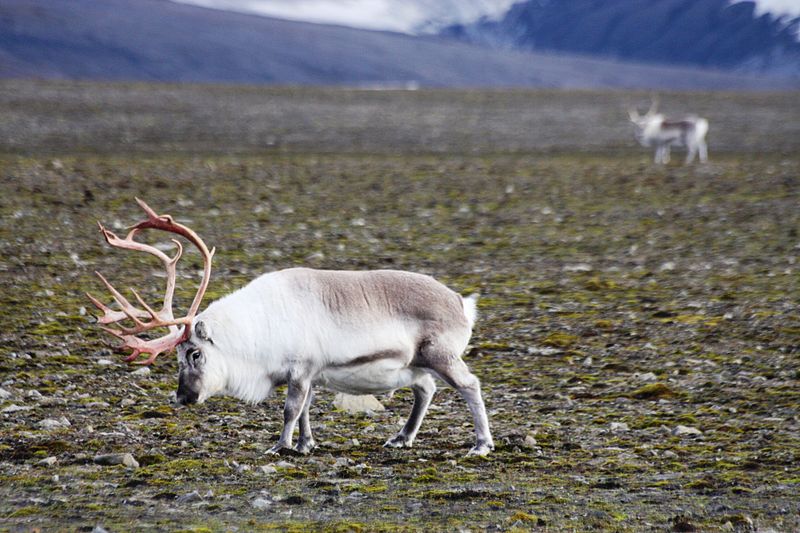

Svalbard reindeer may make short altitudinal movements, or slightly longer inter-island journeys across the sea ice but they are mostly sedentary and therefore have low energy demands. The lack of migration could be a reason why they have evolved short legs, also helping them have conserve heat with a smaller surface area.
However, don’t let their short legs deceive you! They can reach speeds of up to 60 km an hour on a good running surface, giving them the ability to out run a polar bear, the only predator they face on Svalbard (apart from man).
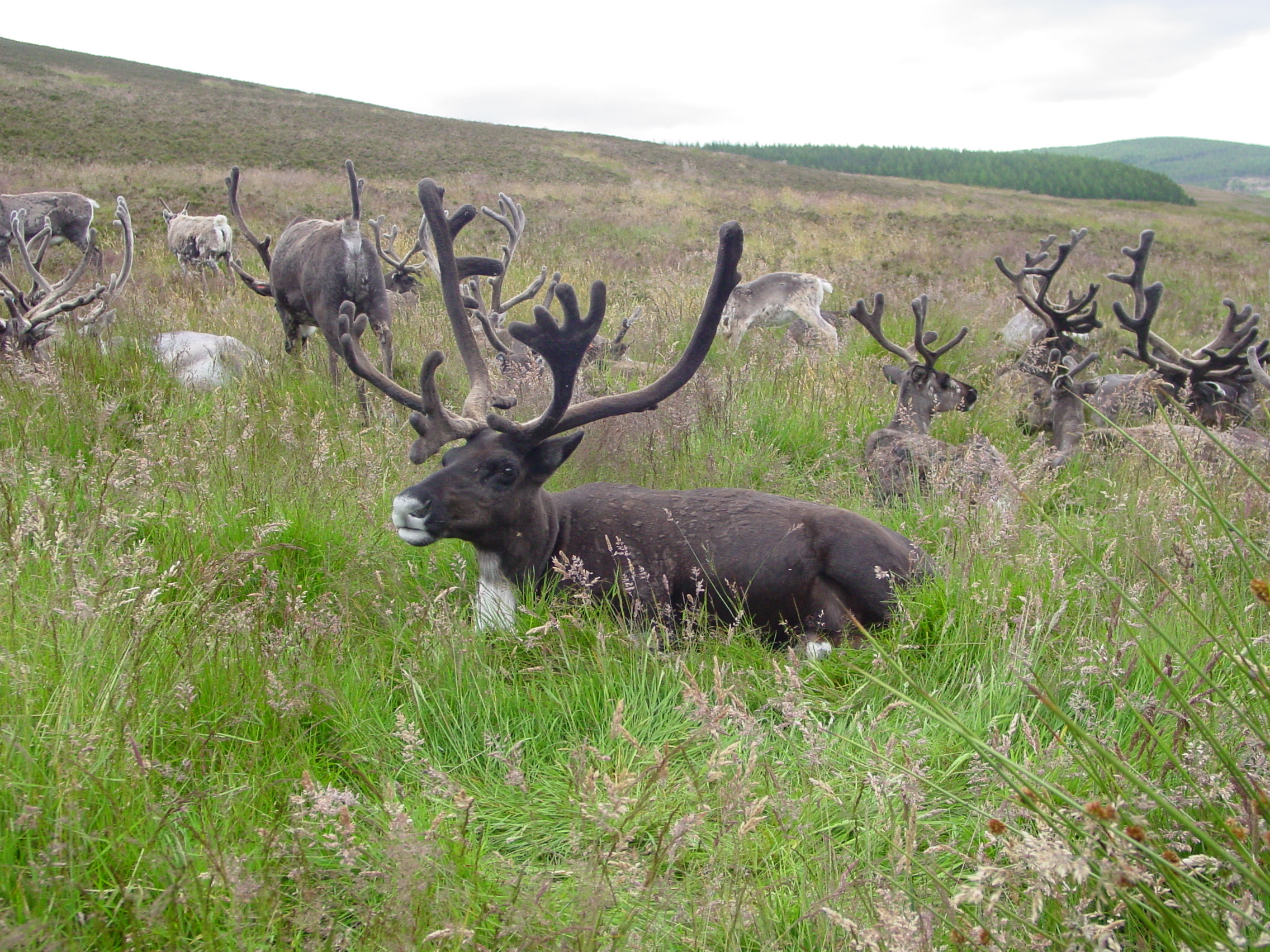
Unlike the majority of Reindeer on the Norwegian mainland the Svalbard Reindeer have not been domesticated, and also do not live in large herds but tend to be solitary or stay in small groups.


I’m digressing, so back to our Scottish Svalbard…

Svalbard was born on the free-range in May 2011 to Arnish, as a result his exact birthday is unknown. Arnish and young Svalbard were not seen between July and October that year, until Svalbard turned up by himself in October at the Hill Enclosure, without his mother, who was sadly not seen again.
When this orphaned calf turned up, he was given a name according to the theme for that year. But the herders at the time kept commenting on how dumpy and short-legged he was; as a result he was quickly nick-named “the Svalbard reindeer”. Before too long, the name stuck and he’s been Svalbard ever since! Thankfully for him, he lost his stocky proportions and we now have a handsome reindeer with a big personally!
This whole blog was basically an excuse to show some cute photographs of a young Svalbard (and to research a future holiday destination!) so here come the pictures…




Ruth