Over the years I’ve established myself as ‘chief of antler sales’ here at the Cairngorm Reindeer Centre. As with most reindeer related things, it’s not really a job that is straight-forward but one that has evolved with time, and I’ve tweaked and tweaked each year until it is as workable as possible. But – in usual fashion – the devil is in the details, much of which are in my head and memory and it’s therefore not a job that I delegate to anyone else.
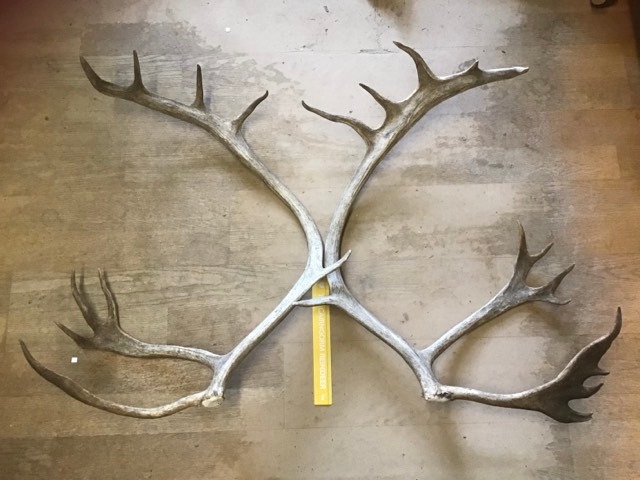

We’ve always sold antlers from the reindeer herd. But is it as easy as 150 reindeer equals 300 antlers per year to sell? Of course it isn’t…
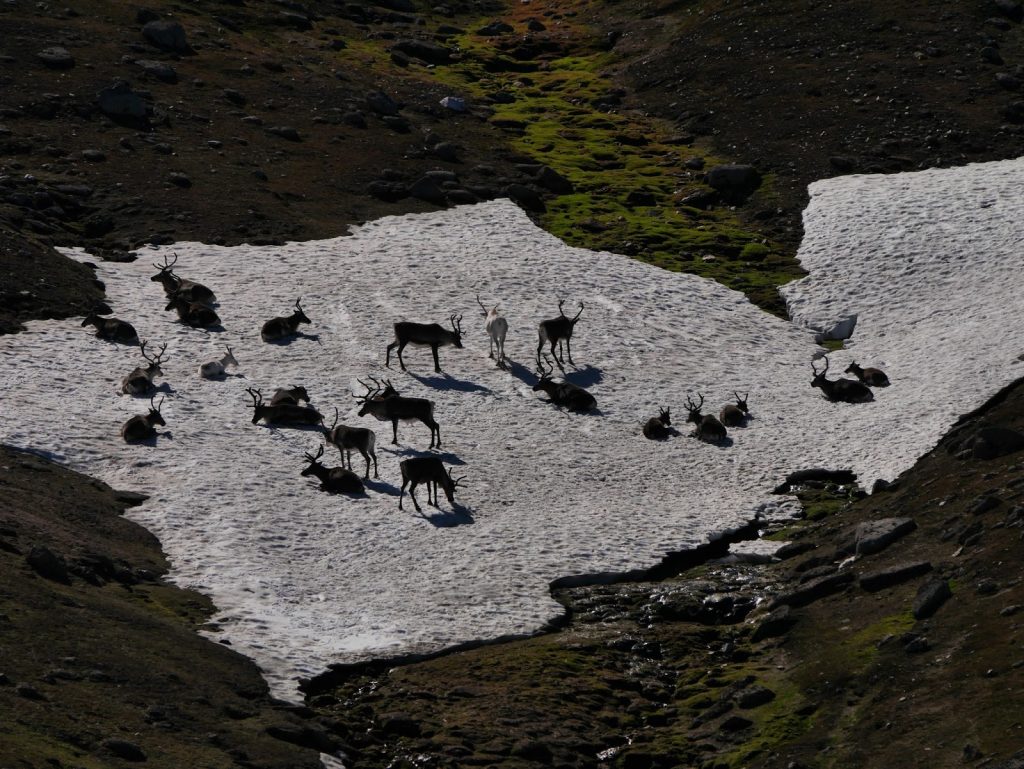
Firstly, we only find around 30-40% (at a rough estimate) of the antlers each year. This is because the reindeer roam on a huge area of rough, upland land, and the time of year when most antlers are shed – January to April – is exactly the time that almost the entire herd are roaming completely freely and are not enclosed at all. The proverbial needle in the haystack. (In fact sometimes finding the herd itself can be a needle/haystack situation, let alone their cast antlers!).
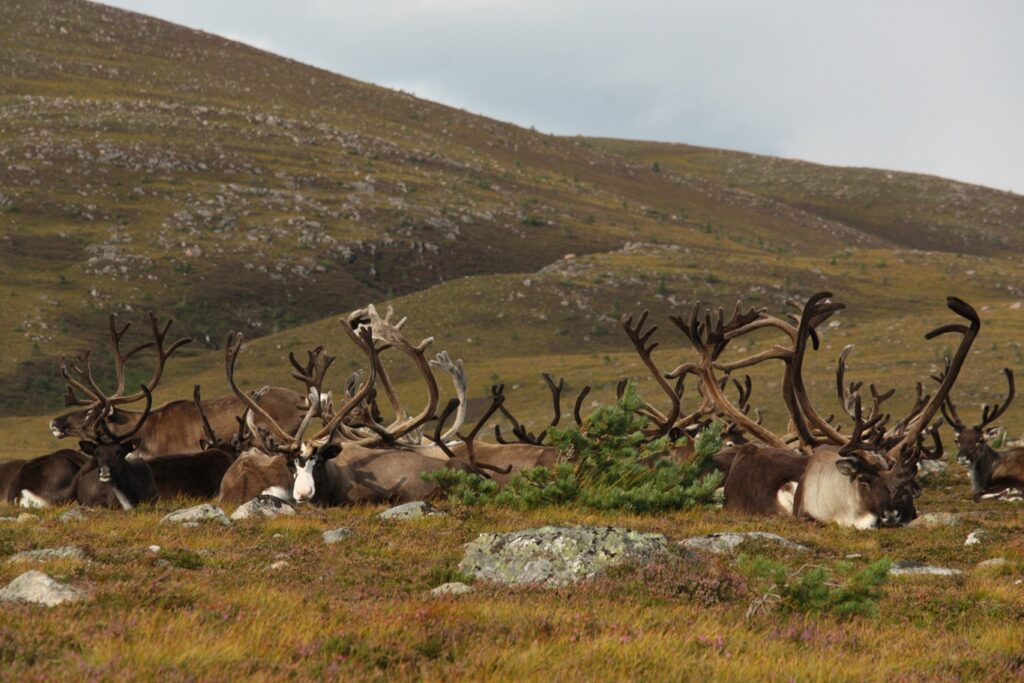

Secondly, whilst around half of our herd are males, we tend to castrate them at around three years old. This means the bone of their antlers doesn’t calcify to the same extent, and they will usually break their antlers off in pieces as a result. So instead of a nice, clean antler, we get broken sections of – to be quite honest – often rather manky antler, still partly covered with the velvet skin that covered it whilst it grew. Smaller pieces disappear into deep vegetation – never to be seen again – far more easily than a whole antler.
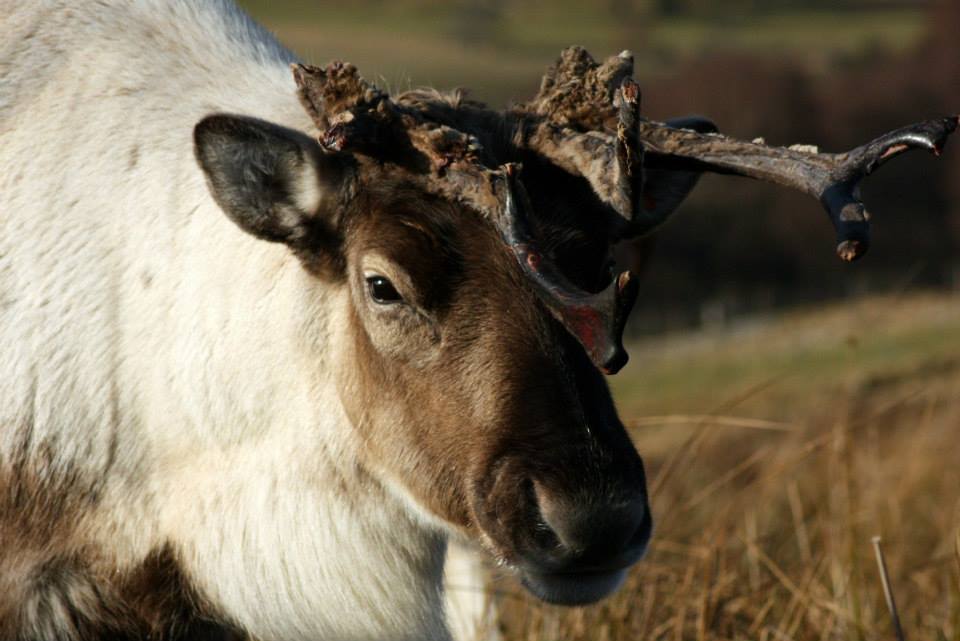


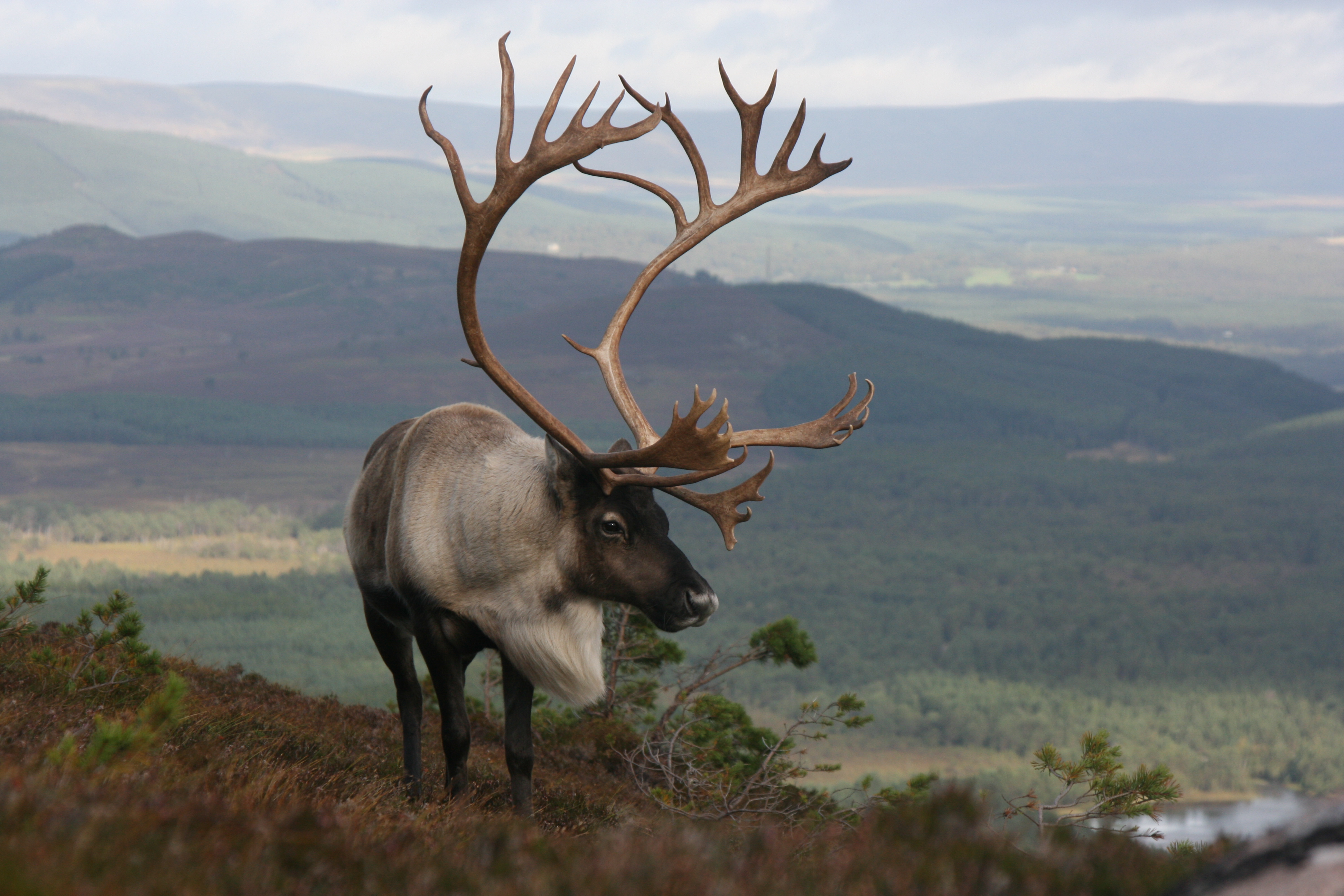
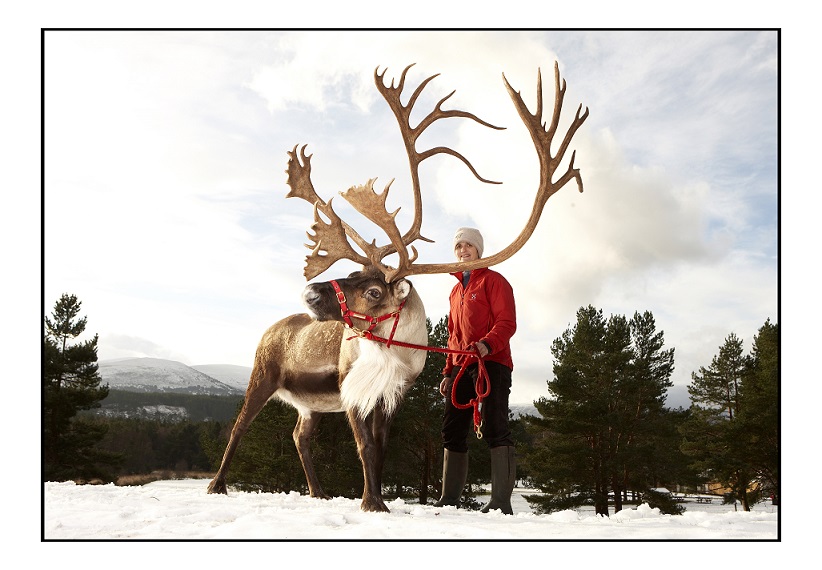
Once castrated, males also tend to grow relatively smaller antlers than they did as a bull. So we really only get two or three big, mature bull sets of antlers each year. But some of these we keep – for example we have almost all of Sherlock’s antlers, and most of Crann’s. Crann holds the record for the biggest antlers ever in the herd, and as such we’ll never sell them as they are of great nostalgic value to us, even though Crann himself is long gone.

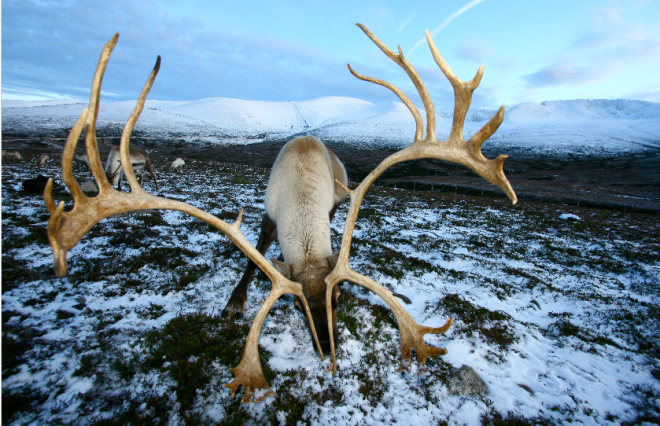
Antler selling starts in January each year. The mature bulls have dropped their antlers in November/December, and some of our immature bulls then have their antlers cut off in December before they are let out to their winter grazing up on the mountains. This is done for the safety of hill-walkers – a testosterone-charged ‘teenage’ bull could really inflict damage. It’s done long after the feeling in the antler has gone, so causes zero pain.
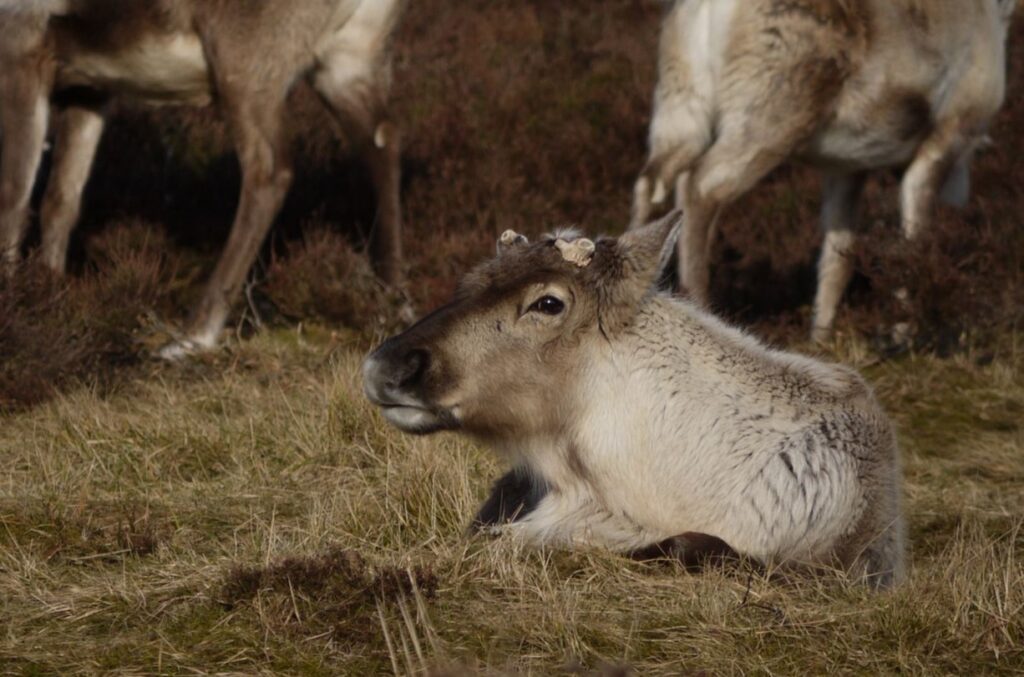

From (usually) around February or March onwards the cows start dropping their antlers, but for me life gets very busy in the spring with the calving season, followed by writing/editing the June newsletter, so it’s often well into the summer before I pick up the antler list once again.
So… here’s some info for those of you now imagining a nice set of antlers adorning your wall.
Firstly, I give members of our reindeer adoption scheme priority for purchasing antlers over ‘unconnected’ members of the public. I feel it’s a privilege someone who supports our business should get. My method for this is to have a waiting list for adopters to add their name for dibs on ‘their’ reindeer’s antlers, which I work my way through gradually as and when I have something suitable. Should you want to add yourself to this list, drop me an email through the contact form on the website FAO Hen (please don’t just comment on the blog/social media – email means I can keep everything together, and gives better chance of a reply one day from me actually reaching you, rather than disappearing into spam).
If you’ve asked to be on the waiting list in the past, no need to get in touch again – you’ll still be there. Well you will as long as your adoption is still current. I’m afraid that I always double-check someone is still an adopter before emailing them, and you’re scratched off the list if your adoption has lapsed. My list, my rules.
If I have no-one on the waiting list for a particular reindeer’s antler(s), then I will send a letter to all of their (UK based) adopters in one go – and it’s first come, first served. Miss out, and you go on the waiting list. This does mean sometime multiple people are all waiting for the same reindeer to shed his/her antlers – which we might never find from year to year anyway. I’m well aware some poor souls have been languishing on the waiting list for years… sorry.
If you aren’t an adopter of a reindeer and are reading this in despair, wondering whether there’s ever a chance of you getting anything, then all is not lost. Email me anyway, and I have a password-protected webpage with any available antlers on that I can give you details of, and on which you can sign up for occasional email alerts when new ones become available (if I get my arse in gear, this is still only two or three times a year, so don’t worry about me flooding your inbox. (Also, I hate Mailchimp – it’s totally user-unfriendly)). I have separate webpages for single antlers and for pairs, and usually have a much better range of single antlers, since finding both sides of a pair is rarer in the first place.
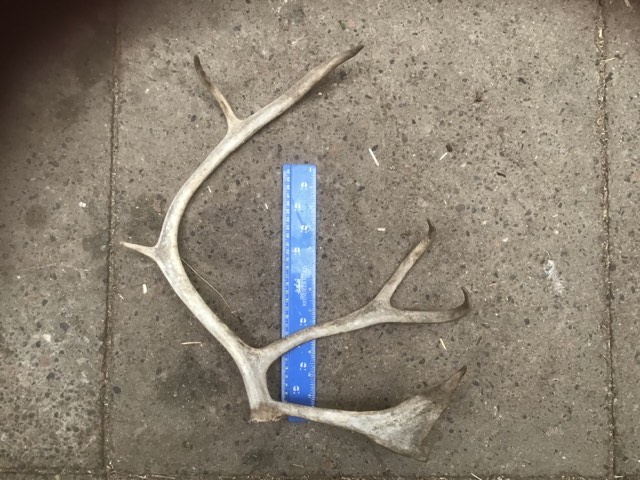

Final info:
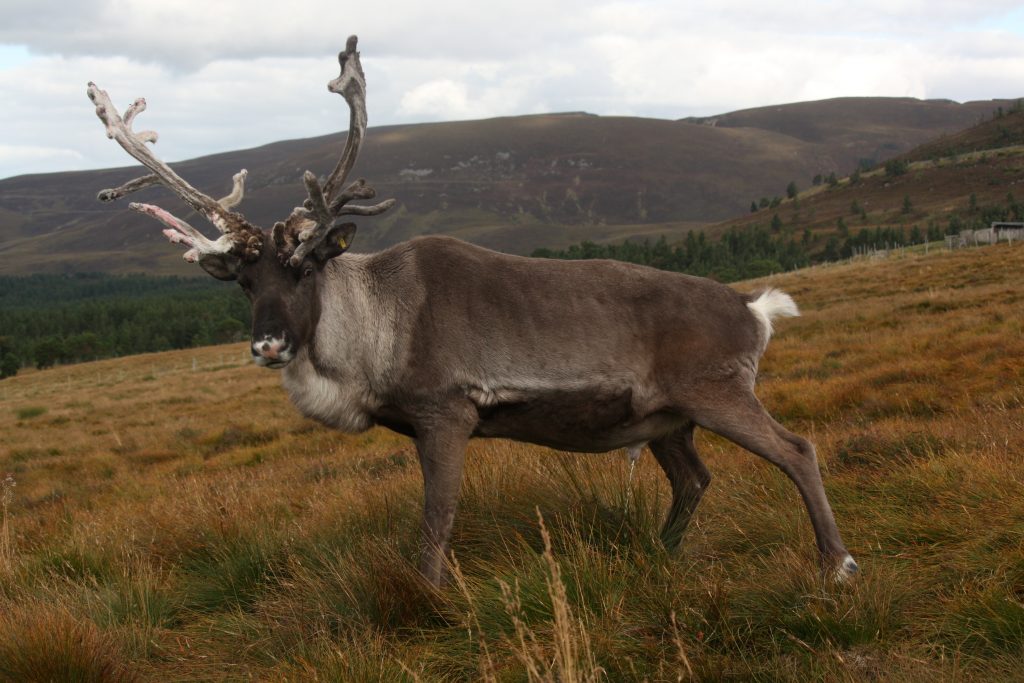
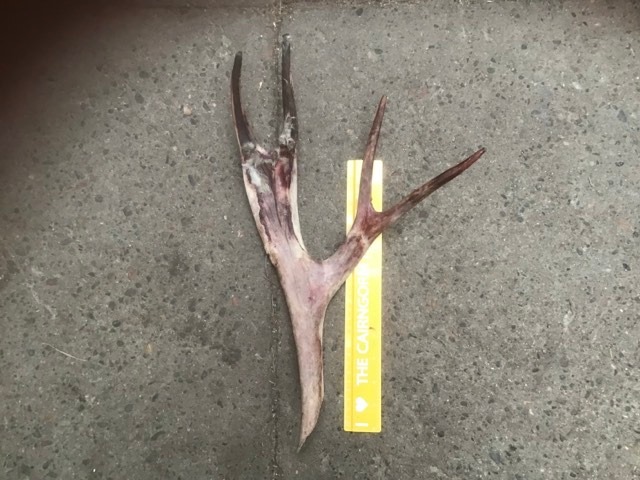
Yes, they do cost a lot. The biggest sets we ever get to sell are in the region of (at time of writing in 2024) £300. The single antler in the photo above was about £60. I guess other places with reindeer in the UK maybe also sell their antlers, but I’ve never actually heard of them doing so. I do my best to price antlers fairly though – every single one is utterly unique and in some way it is a snapshot of that reindeer at that particular point of their life. I’m sure I could push up the prices hugely and they would still sell eventually, but that isn’t the point. It’s a balancing act to try and get it right.
For adopters, if you perhaps can’t afford the antler(s) you been contacted about, it’s still worth going on the waiting list. I might have a glorious £200 set of beautiful antlers one year from your reindeer, and a single broken-off – much cheaper – half antler the next year. But hey, it’s still a piece of antler that your reindeer actually grew, and really it means just as much.
Conversely, you miss out on something small that you had your heart set on. But hey presto you might then be first in line for the potentially much more impressive effort from your reindeer next year. It’s all utterly unpredictable and there’s definitely an element of luck involved.
I can’t post abroad, sorry.
If you can collect your antler(s) rather than me having to package and post them, a) it’s cheaper and b) I love you.

If you receive an ‘antler letter’ through the post – read it properly! I always do my best to describe the antler fully before you phone up to buy it – but have never forgotten the lovely couple who arrived to pick up a set of antlers from their adopted reindeer years ago. The bloke was a bit worried about fitting them in the car. The antlers were about 30cm tall.
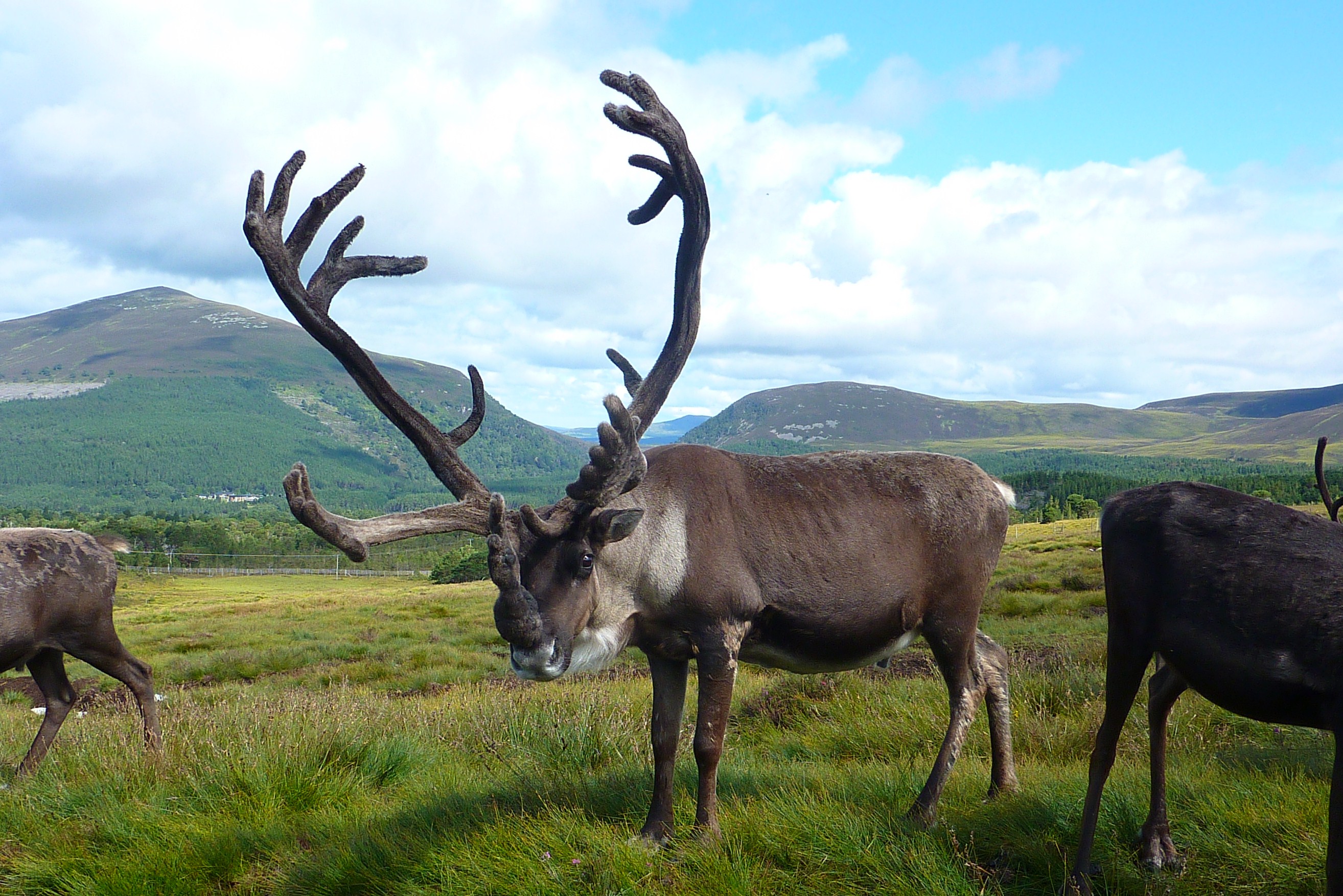
Antlers come in all sizes but all shapes too. Forget that classic set of ‘perfect’ shapely reindeer antlers you’ve got in your mind’s eye – they probably aren’t going to look like that… If I’m emailing you directly I’ll attach a photo, and if I’ve sent you a letter, you can ask to see a photo before you decide.
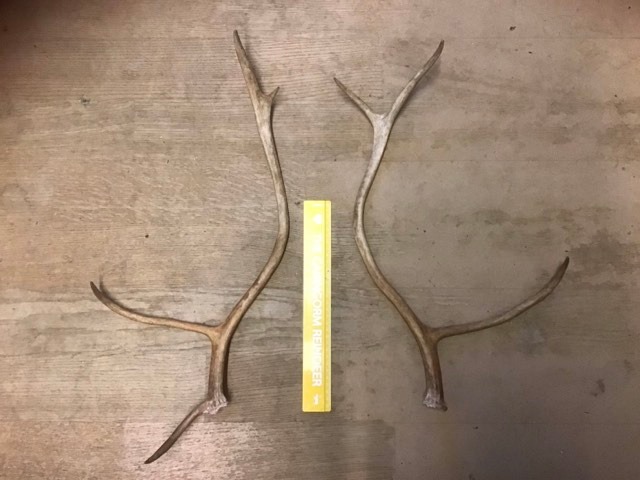
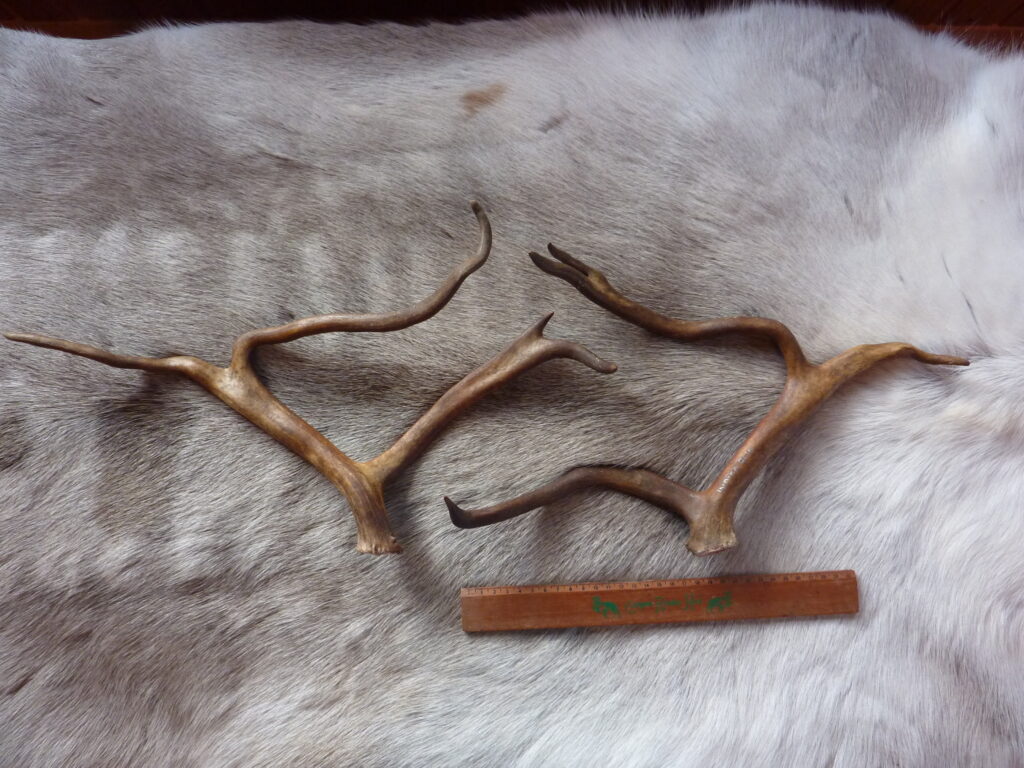


As mentioned before, we keep some of the biggest bull antlers. Herders also usually have first dibs on their favourite reindeer’s antlers (I’ll add that (depending on the size of antler) we do usually still have to pay for them!), so there are certain reindeer in the herd whose antlers will come up for sale very rarely, if ever. Huge apologies, if you also adopt one of those reindeer… let’s mention no names.
I do also try to be fair to people – if I know you already have multiple antlers from a certain reindeer but are keen for more, I will usually try and give their other adopters a look in at some point.
And if you adopt Juniper, well don’t give up hope. Ferrari was also a ‘polled’ reindeer (one who doesn’t grow antlers at all) and suddenly sprouted one when she reached 9 years old, so all is not lost. But I wouldn’t get your hopes up too much.

And finally, I’m only human so bear with me as the old brain doesn’t get everything right every time. Apologies again to the lovely lady who I posted the entirely wrong set of antlers to a couple of years ago, and then had to go through a whole rigmarole of getting her to post them on to the correct new owner (Editor’s note: we did get permission to pass on the address first!), whilst I sorted out the right set for her. And years ago I died a little bit inside when I realised we’d sold the same antler to two separate people, and I was going to have to make a very awkward phone-call (although in my defence, it wasn’t actually me that forgot to mark that antler as ‘sold’ on the list). Oh, the horror.
Hen