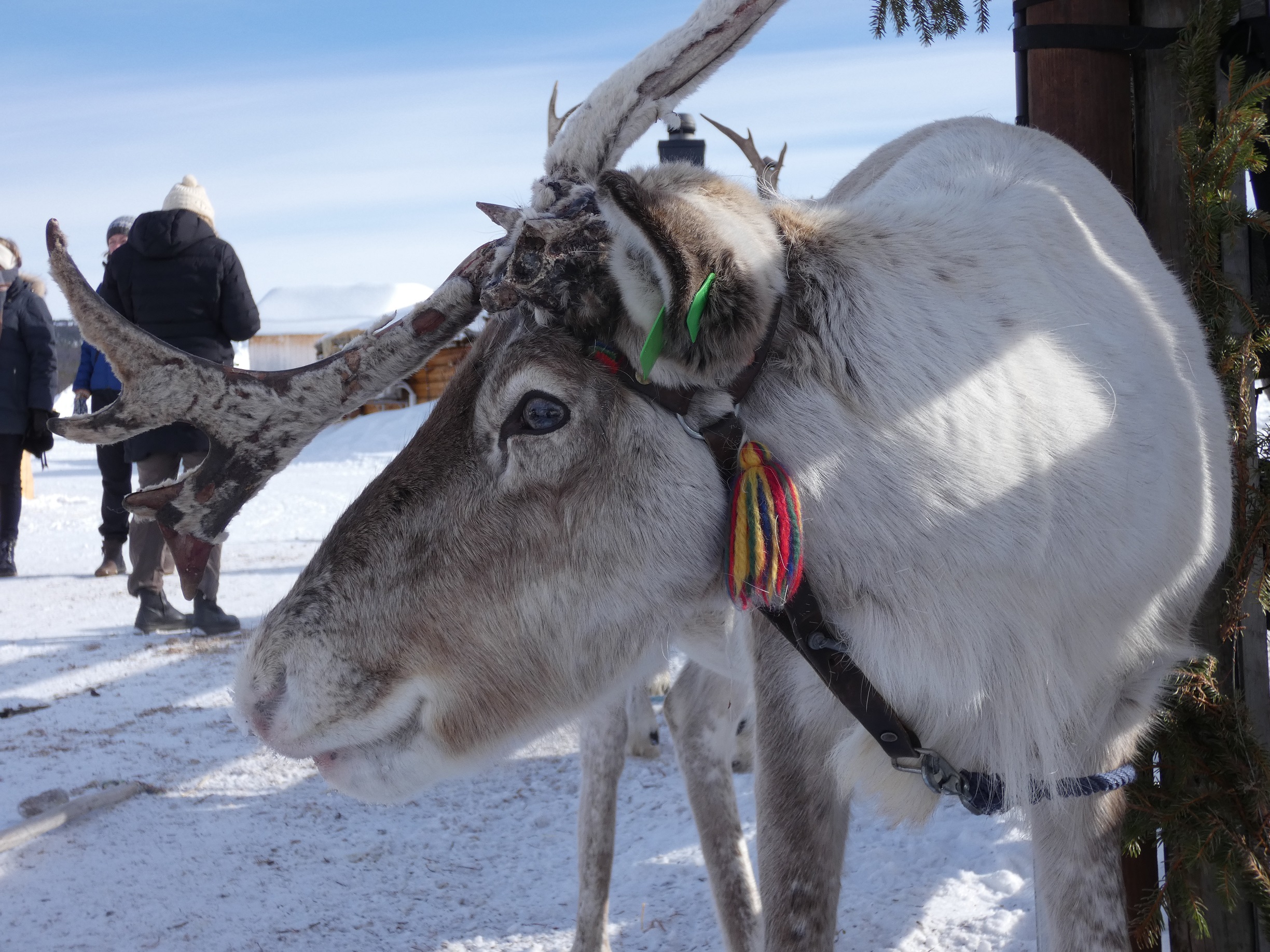
On our kids quiz in the Paddocks is the question ‘Name a sub-species of reindeer’, and I notice it’s often the one that people get stuck at (despite the fact that the answers are there on the display boards). I’ve realised over the years however, that this is often down to a basis lack of understanding of a percentage of the population of the concept of species and sub-species, rather than anything else. So therefore, allow me to explain.
As a zoology student (all too many years ago, so bear with me if my science is rusty!), the classification of all organic species using a system of ‘taxonomic rank’ was drilled into us. The system still in use today was founded by Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus in the 16th Century and brought order and clarity to the then chaotic and disorganised way of naming and categorizing all types of life. No wonder I loved learning about taxonomy – lists and organisation? My kinda thing.

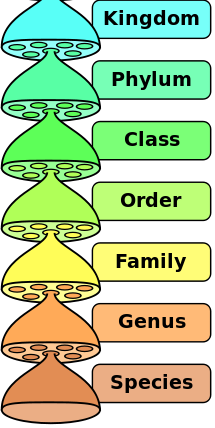
The Linnaean system breaks down all living things into 7 major kingdoms, animals being one and plants another, and then each kingdom is broken down further, into different phyla. Then phyla are broken down once more to the next level, which is class, and the system carries on through order; family, genus and finally species. So reindeer can be categorized as such:
Kingdom: Animalia (Common name: Animals)
Phylum: Chordata (Chordates – meaning ‘possessing a nerve cord’)
Class: Mammalia (Mammals)
Order: Arteriodactyla (Even-toed hooved mammals)
Family: Cervidae (the Deer family)
Genus: Rangifer
Species: tarandus
The two part ‘binomial’ name Rangifer tarandus is perhaps more commonly known as a ‘Latin name’, and every species in the world has one. You will be familiar with ours as Homo sapiens, and like humans, reindeer are the only species within their genus, Rangifer. A regular question from visitors is ‘So….how are reindeer different from deer?’ Bizarrely, it can be quite hard explaining to people that reindeer are deer. My usual analogy is to get people to think about lions and tigers. Both obviously cats, so therefore members of the cat family (‘Felidae’), but at the same time both clearly different species from each other. So while reindeer are a member of the deer family, they are a different species from other types of deer. For example, moose, red deer and muntjac – all clearly distinguishable in looks from one another, but crucially also genetically different.
But then, as with most things, it all gets a little more complicated. Not content with 7 major divisions, scientists introduced sub-divisions in order to break down everything further. So now there are, among others, sub-classes, sub-families, sub-genera etc. Arghh! While Rangifer has no sub-genus, there are some subspecies to contend with, and this is the relevant info that we hope people will track down in our Paddocks. All seven subspecies of reindeer and caribou are all still Rangifer tarandus, so effectively all genetically the same animal, but a subspecies is shown by adding a third name after the binomial. Just to clarify too, reindeer and caribou are the same animal, but reindeer are the domesticated version of caribou. The differences are also geographical, in that reindeer are found in Europe and Asia, while caribou are found in North America and Greenland.
So back to our seven subspecies. We have:
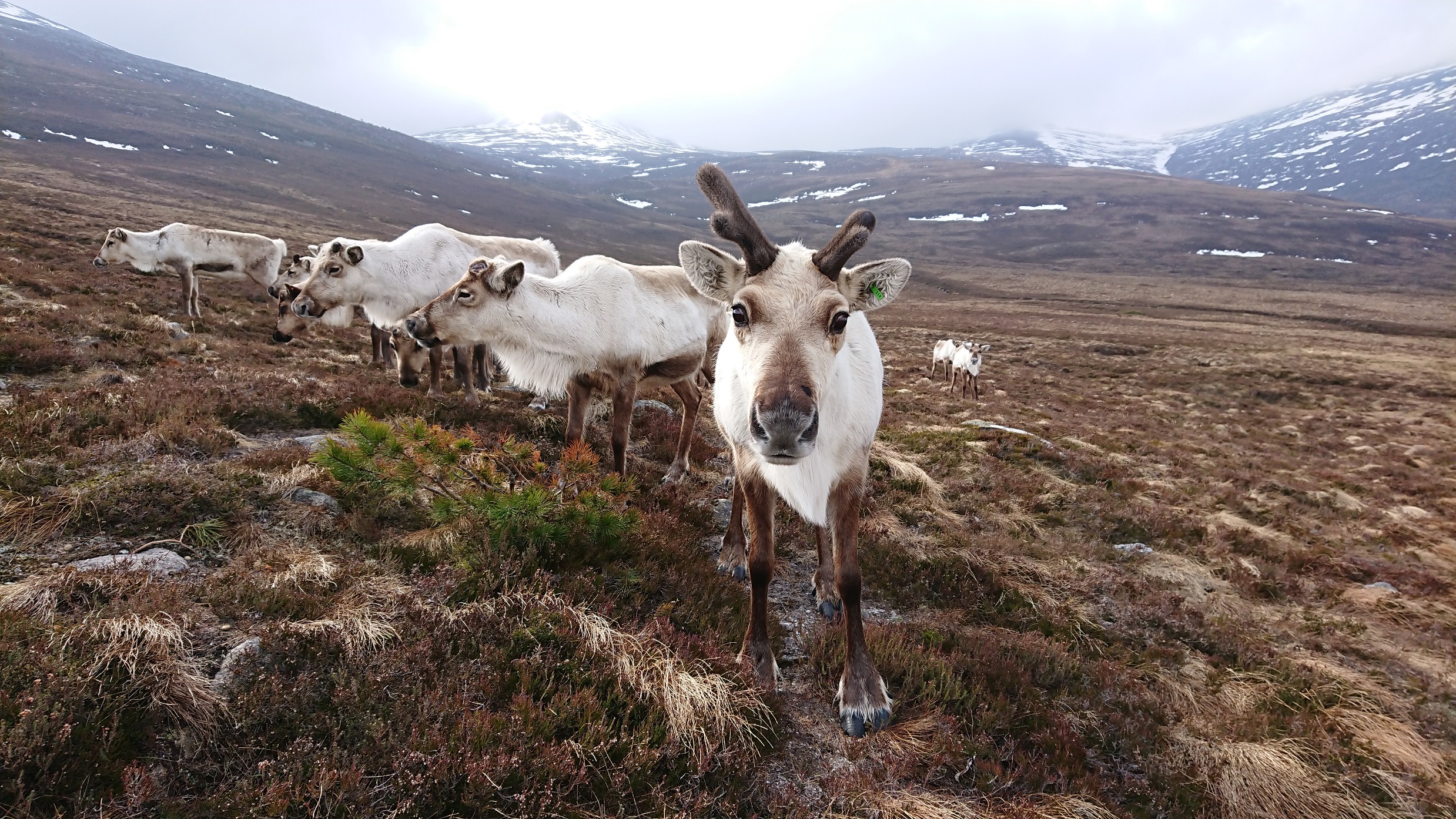
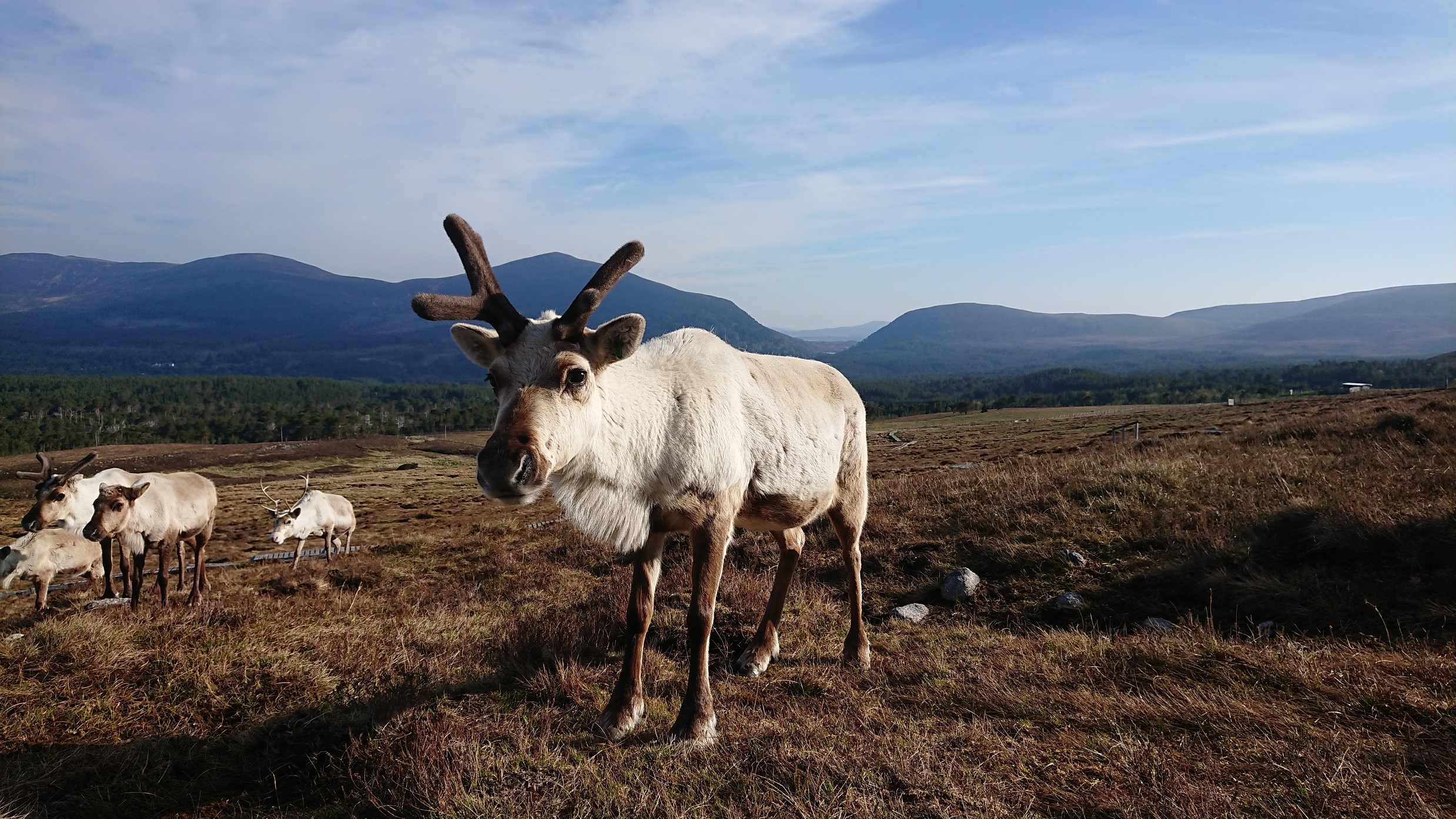
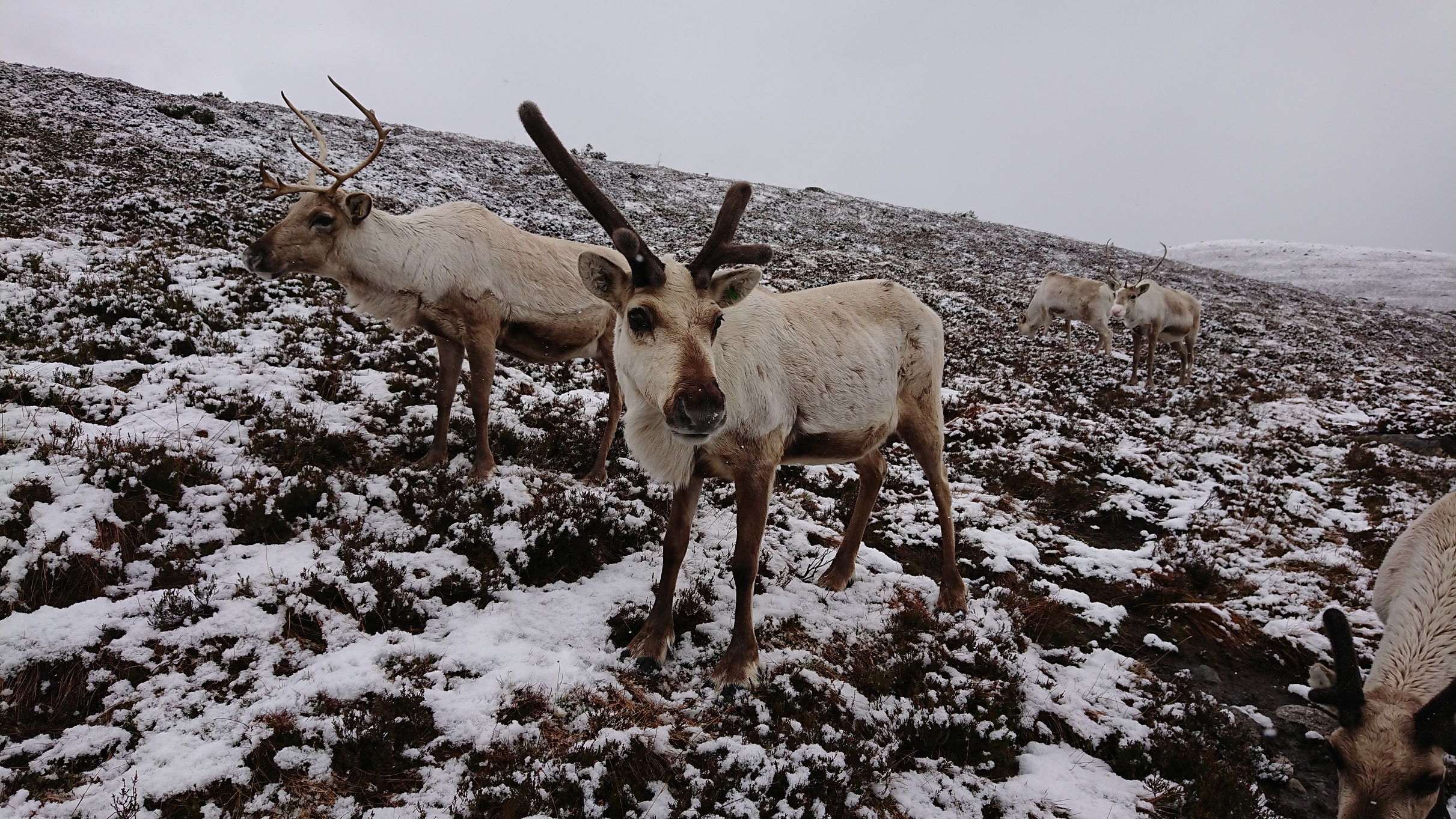
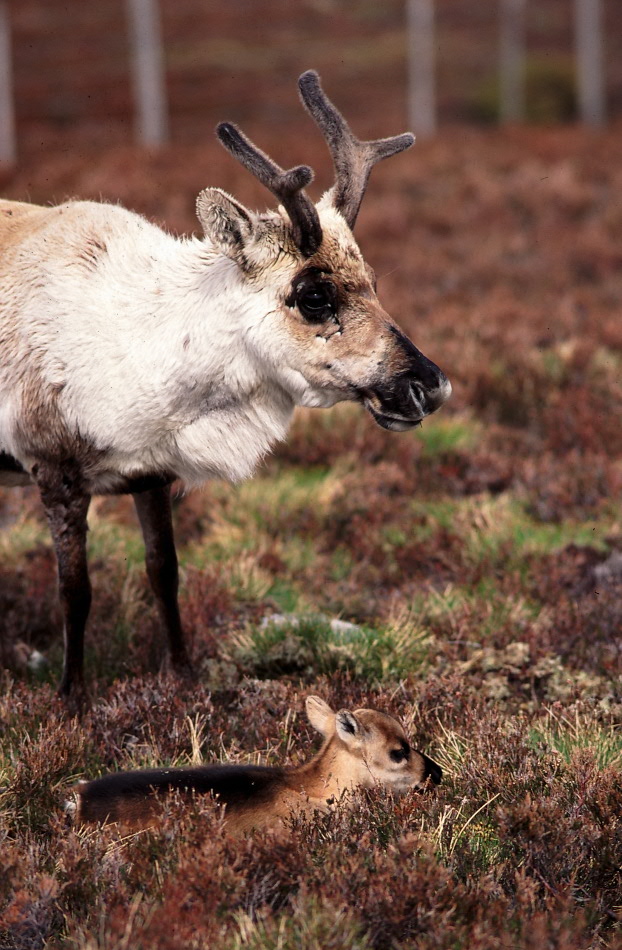
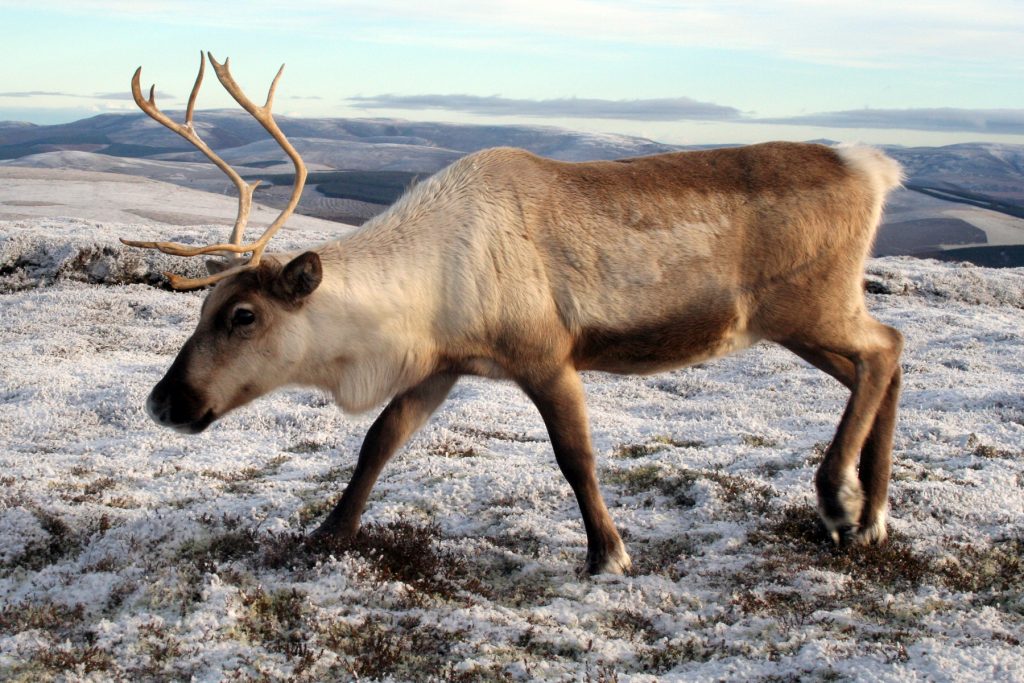
Eurasian Tundra reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus): Open-ground dwelling subspecies, which the majority of all domesticated reindeer belong to, including ours.
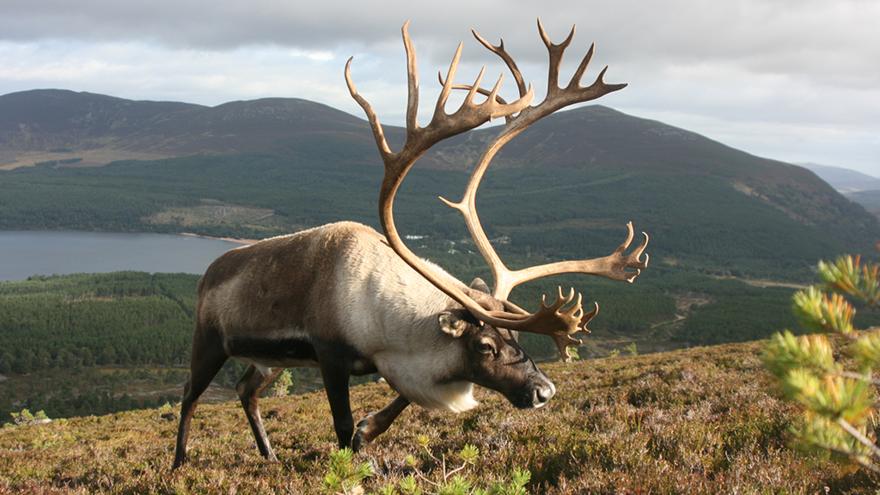

Eurasian Forest reindeer (Rangifer tarandus fennicus): Boreal forest dwelling subspecies, typically taller than tundra reindeer.
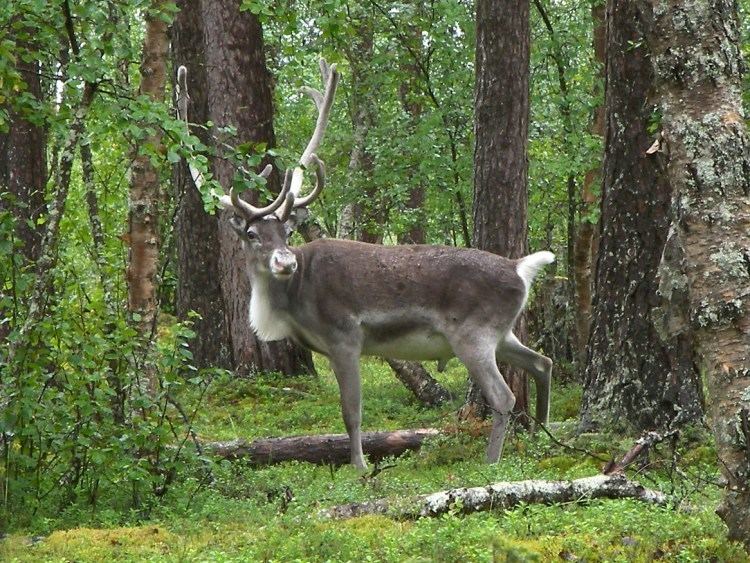

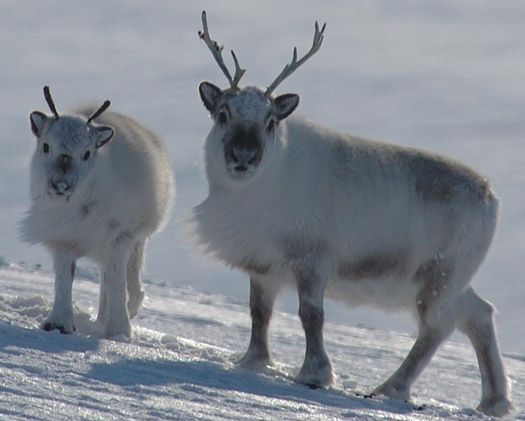
Svalbard reindeer (Rangifer tarandus platyrhynchus): Smallest subspecies, endemic to the arctic archipelago of the Svalbard islands. Short legged!

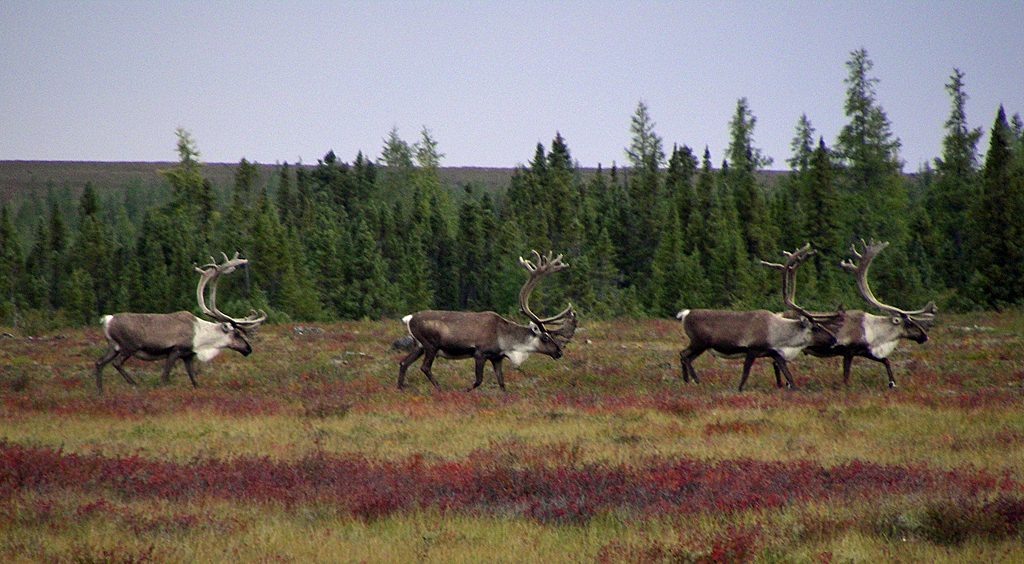
Barren-ground caribou (Rangifer tarandus groenlandicus): Migratory subspecies of open ground. The most similar of the caribous to our tundra reindeer.

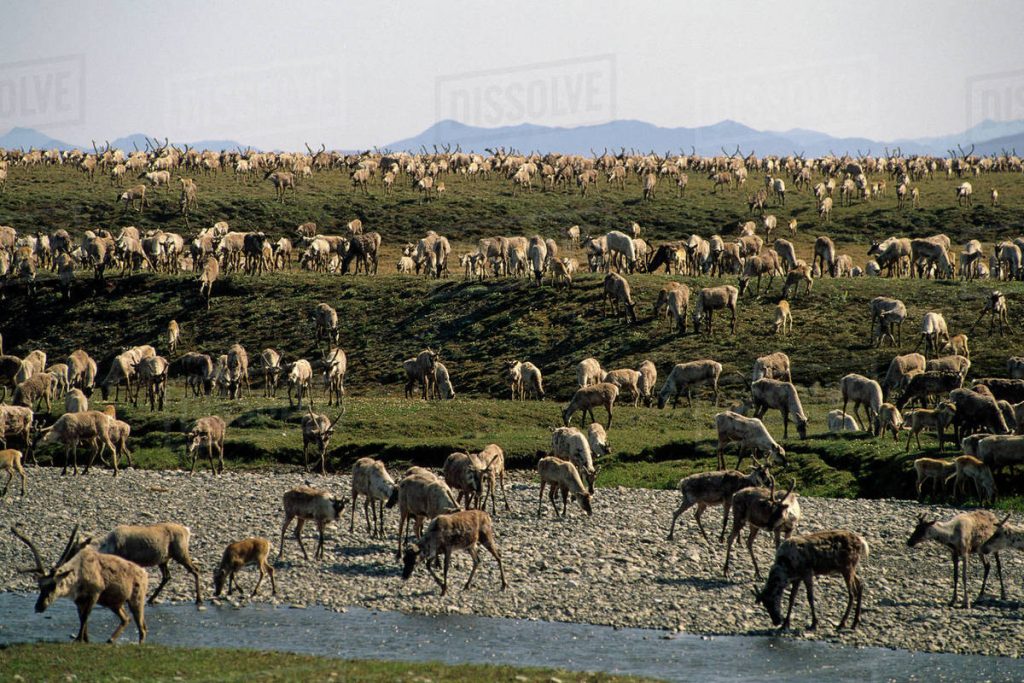
North American woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou): Largest caribou subspecies, often darker in colour. As the name suggests, they live in forests, and generally don’t migrate.

Peary caribou (Rangifer tarandus pearyi): Smallest of the caribou subspecies.

Alaskan or Porcupine caribou (Rangifer tarandus granti): Migratory subspecies most closely resembling the barren-ground caribou, and named after the Porcupine river, which runs through much of their range. The longest migrating land mammal on Earth.

There have been two other subspecies in the past but these have now died out – the East Greenland Caribou and the Queen Charlotte Island Caribou.
So there you go, a brief taxonomy lesson, and congratulations to anyone who has stuck with me, as well as apologies for some slight over-simplifications for any scientists amongst you. Hopefully you’ll have all learnt something though – I’m a big believer of sneaking in educational blogs among the pretty pictures and funny stories we often post! And if it’s all too much and you’d just prefer something a bit more light-hearted, head off and google pictures of Svalbard reindeer. You’ll not be disappointed.
Hen